Hormone
Ethylene (ET)

The earliest discovery of Ethylene occurred when when lamp post near a greenhouse caused wilting and leaf abscission. - a wikimedia commons image
Chemical Structure
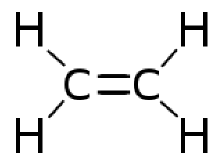
Ethylene is an extremely simple gas
- a wikimedia commons image
Speculative Overall Role
Oxygen and maybe other gas deficiency signal
What is Ethylene's speculative
complementary abundance signal?
Auxin (IAA)
If overall speculative role is true, where,
when and which cells should synthesize Ethylene?
Cells most apt to be oxygen deficient are the interior of roots and flooded roots in general.
If overall speculative role is true, what
should exogenous Ethylene treatment produce?
Exogenous ethylene treatment should show methods for increasing oxygen to the roots such as Aerenchyma tubes or increasing leaf area. Additional measures might include epinasty for pumping out extra water from around the roots, metabolism inhibition and photosynthesis stimulation.
If overall speculative role is true, what
should Ethylene inhibit and stimulate?
Ethylene should inhibit root growth and encourage shoot growth. It should inhibit metabolism and stimulate photosynthesis. It also is known to stimulate the growth of root hairs, a method for increasing the surface area of the root and its absorption of oxygen for local use.
If overall speculative role is true,
how should Ethylene affect storage?
Ethylene should cause the release of stored Oxygen if there is such a thing.
If overall speculative role is true,
how should Ethylene be transported?
Ethylene should be transported from the roots to the shoots, perhaps by rising or bubbling up from the ground as a gas or being transported up as ACC.
If overall speculative role is true, how should
Ethylene affect attraction and repulsion?
Ethylene should generally push nutrients and stimulating/growth hormones out of cells and attract deficiency hormones. Possibly it works with Auxion producing leaves to attract more nutrients to these Oxygen harvesting sites.
If overall speculative role is true, how
should Ethylene affect apical dominance?
Ethylene represents a failure of the current methods for harvesting Oxygen, therefore it should break the apical dominance induced by Auxin.
If overall speculative role is true, how
should Ethylene affect Cell Division?
Ethylene should generally inhibit cell division although it may stimulate it in shoot areas that are particularly efficient at harvesting Oxygen and therefore making Auxin.
If overall speculative role is true, how
should Ethylene affect senescence?
Ethylene should inhibit root growth along with Gibberellin and cause the senescence of older roots. It should inhibit the senescence of shoots parts, especially those making Auxin.
If overall speculative role is true,
how should Ethylene effect growth
directions to provide balance in the plant?
Ethylene is known to broaden plant parts. Its analogue stimulating hormone, Auxin, appropriately lengthens plant cells and tissues.
Proven Synthesis and Transport
-
Induced by high levels of Auxin, especially in the roots but this can be moderated by red light which characteristic of shading. 55 Why this makes sense -
-
Ethylene levels increase during flooding, probably due to entrapment rather anoxia. Most plant appear to have a net inhibition of Ethylene production under anoxic or carbon dioxide deficient conditions. 56 Why this makes sense -
Proven Effects
-
Promotes the ripening of fruit with climacteric respiration releasing additional ethylene. 52 Why this makes sense -
-
Inhibits leaf expansion. 54 Why this makes sense -
-
Inhibits geotropism. 55 Inhibits Auxin transport 55 and production? Why this makes sense -
-
Induces leaf, fruits, and flower petal abscission. 52 Why this makes sense -
-
Flooding produces the epinasty reaction through Ethylene, where leaf surfaces deliberately grow from a position perpendicular to the stem to one which is more horizontal. 52 58 Why this makes sense -
-
Induces air spaces called Aerenchyma used for gas diffusion in roots during flooding of non-water based plants. 59 Why this makes sense -
-
Carbon Dioxide inhibits Ethylene action. 58 Why this makes sense -
-
Inhibits embryogenesis of cell cultures. 60 Why this makes sense -
-
Induces root hair growth. 61 Why this makes sense -
-
Ethylene up-regulates Auxin biosynthesis at least in the roots. 61 Why this makes sense -
-
Flood induce ethylene sensitizes plants to the existing steady Auxin levels, inducing adventitious roots formation. 62 Why this makes sense -
-
Induces flower formation in some species. 52 63 Why this makes sense -
-
Etephon (ethylene precursor) has a dual role in tuberization. It promotes already formed tubers by inhibiting stolon growth. Differently though it inhibits the formation of new tubers. 64 Why this makes sense -